Abstract
Introduction: Certain fermented dairy milk products may have beneficial effects on plasma cholesterol levels. However, a number of studies have produced conflicting results as to whether dietary supplementation by a probiotic dairy product containing the bacteria culture Causido® reduces plasma cholesterol.
Objective: To conduct a meta-analysis of intervention studies to evaluate the effect of the Causido® culture on plasma total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein (LDL)-cholesterol.
The probiotic milk product: The yoghurt product Gaio® is fermented with Causido®, composed of one strain of Enterococcus faecium (human species) with the proposed cholesterol-lowering effect, and two strains of Streptococcus thermophilus.
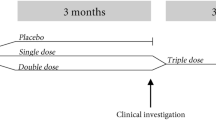
Study inclusion and data extraction: Six studies were identified from a literature search and from the yoghurt producer. All studies met the inclusion criteria. Summary data for plasma concentrations of total cholesterol and LDL-cholesterol were extracted from the original publications or by personal request to the authors. Data from 4–8 weeks of treatment duration was used.
Statistical analysis: We performed a traditional meta-analysis where mean differences between intervention and control of the pre–post changes in total cholesterol and LDL-cholesterol were calculated, as well as 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Results: In the six studies included in the meta-analysis, the Gaio® interventions produced changes in total cholesterol above those of the control groups ranging from −0.02 to −1.02 mmol/l and in LDL-cholesterol ranging from −0.02 to −1.15 mmol/l. After inclusion of an open-label study, the meta-analysis of the double-blind studies showed that Gaio® as compared to the control group changed total cholesterol by −0.22 mmol/l (95% CI: −0.35 to −0.08, P<0.01) and LDL-cholesterol by −0.20 mmol/l (95% CI: −0.33 to −0.06, P<0.005). The outcome was essentially the same if all studies were included.
Conclusions: The present meta-analysis of controlled short-term intervention studies shows that the fermented yoghurt product produced a 4% decrease in total cholesterol and a 5% decrease in LDL-cholesterol when the open-label study is excluded. To demonstrate sustained effects on blood lipids, long-term studies are required.
Sponsorship: MD Foods A/S, Denmark.
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2000) 54, 856–860
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Guarantor: A Astrup.
Contributors: A Astrup and L Agerholm Larsen initiated the project. L Agerholm Larsen was responsible for data collection and manuscript preparation in collaboration with A Astrup. M Bell and GK Grunwald were responsible for the statistical analyses. All authors were involved in the final edition of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agerholm-Larsen, L., Bell, M., Grunwald, G. et al. The effect of a probiotic milk product on plasma cholesterol: a meta-analysis of short-term intervention studies. Eur J Clin Nutr 54, 856–860 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601104
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601104
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Nutraceuticals in the Management of Dyslipidemia: Which, When, and for Whom? Could Nutraceuticals Help Low-Risk Individuals with Non-optimal Lipid Levels?
Current Atherosclerosis Reports (2021)
-
Yogurt Intake Reduces All-Cause and Cardiovascular Disease Mortality: A Meta-Analysis of Eight Prospective Cohort Studies
Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine (2020)
-
Effects of products designed to modulate the gut microbiota on hyperlipidaemia
European Journal of Nutrition (2019)
-
The use of probiotics for improving lipid profiles in dyslipidemic individuals: an overview protocol
Systematic Reviews (2018)
-
The Effects of Synbiotic Supplementation on Glucose Metabolism and Lipid Profiles in Patients with Diabetes: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins (2018)