Abstract
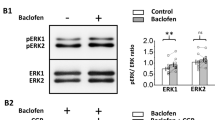
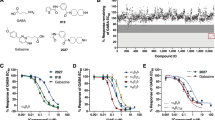
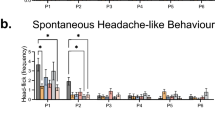
The existence of a receptor for γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) on neurones of the mammalian central nervous system (CNS) is now firmly established1–3. It is generally accepted that bicuculline (and its methohalide salts) is an antagonist of the actions of GABA4,5, although resistance to bicuculline has been described6,7. The view that bicuculline prevents GABA from interacting with a membrane recognition site is supported by results obtained in radiolabelled ligand binding studies8,9. Bicuculline-sensitive GABA receptors are not confined to neurones in the CNS but are also present on neurones and axons of the peripheral nervous system10,11. Their existence on neurones in sympathetic ganglia made us consider the possibility that they are also present on the terminals of such neurones. This has recently been tested12,13 by assuming that if GABA depolarises the terminals in a manner similar to the cell bodies, evoked transmitter output might be decreased (see ref. 14). GABA (ED50, 4µM) clearly decreased the evoked release of accumulated 3H-noradrenaline from rat atria in vitro and 3H-acetylcholine from preganglionic terminals in the rat superior cervical ganglion in vitro without affecting the basal release of tritium. In neither system was the effect of GABA antagonised by bicuculline methobromide, even though the ganglion terminal depolarisation was13. This suggested that the two phenomena, depolarisation and inhibition of transmitter release, were separate. The decrease in transmitter release not surprisingly leads to a decrease in the postsynaptic response15. Again, the decrease in response was not prevented by bicuculline or other GABA antagonists. We believe that these results indicate the presence of a novel GABA receptor on nerve terminals, a theory supported by results obtained with a variety of GABA analogues. For example, 3-aminopropane sulphonic acid (3-APS) which is at least as active as GABA at bicuculline sensitive sites10,16,17 is inactive at the terminal receptor. By contrast, the analogue baclofen (β-chlorophenyl GABA) is inactive at bicuculline-sensitive sites18,19 but is as active as GABA in reducing evoked transmitter output15. This effect of baclofen is stereospecific, the (−) isomer being > 100-fold more active than the (+) isomer15. We now report the presence of the novel GABA receptor within the mammalian CNS.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Curtis, D. R. & Johnston, G. A. R. Ergebn. Physiol. 69, 97–188 (1974).
Roberts, E., Chase, T. N. & Tower, D. B. GABA in Nervous System Function (Raven, New York, 1976).
Krogsgaard-Larsen, P., Scheel-Kruger, J. & Kofod, H. GABA-Neurotransmitters (Munksgaard, Copenhagen, 1979).
Curtis, D. R., Duggan, A. W., Felix, D. & Johnston, G. A. R. Brain Res. 32, 69–96 (1971).
Johnston, G. A. R. et al. Nature new Biol. 240, 219–220 (1972).
Godfraind, J. M., Krnjevic, K., Maretic, H. & Pumain, R. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmac. 51, 790–797 (1973).
Straughan, D. W., Neal, M. J., Simmonds, M. A., Collins, G. G. S. & Hill, R. G. Nature 233, 352–354 (1971).
Zukin, S. R., Young, A. B. & Snyder, S. H. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 71, 4802–4807 (1974).
Enna, S. J., Beaumont, K. & Yamamura, H. I. in Amino Acids as Chemical Transmitters (ed. Fonnum, F.) 487–492 (Plenum, New York, 1978).
Bowery, N. G. & Brown, D. A. Br. J. Pharmac. 50, 205–218 (1974).
Brown, D. A. & Marsh, S. Brain Res. 156, 187–191 (1978).
Bowery, N. G. & Hudson, A. L. Br. J. Pharmac. 66, 108P (1979).
Brown, D. A. & Higgins, A. J. Br. J. Pharmac. 66, 108P–109P (1979).
Dudel, J. & Kuffler, S. W. J. Physiol., Lond. 155, 543–562 (1961).
Bowery, N. G. et al. Br. J. Pharmac. 67, 444P–445P (1979).
Curtis, D. R., Phillis, J. W. & Watkins, J. C. Br. J. Pharmac. 16, 262–283 (1961).
Möhler, H. & Okada, T. in Amino Acids as Chemical Transmitters (ed. Fonnum, F.) 493–498 (Plenum, New York, 1978).
Fox, S., Krnjevic, K., Morris, M. E., Puil, E. & Werman, R. Neuroscience 3, 495–515 (1978).
Curtis, D. R., Game, C. J. A., Johnston, G. A. R. & McCulloch, R. M. Brain Res. 70, 493–499 (1974).
Anderson, S. D. & Roberts, P. J. Br. J. Pharmac. 64, 429P (1978).
Kerwin, R. & Pycock, C. in Baclofen: Spasticity and Cerebral Pathology (ed. Jukes, A. M.) 23–37 (Cambridge Medical Publications, Northampton, 1978).
Kerwin, R. & Pycock, C. Br. J. Pharmac. 63, 388P–389P (1978).
Martin, I. L. & Mitchell, P. R. Br. J. Pharmac. 66, 107P (1979).
Martin, I. L. & Mitchell, P. R. Br. J. Pharmac. (in the press).
Stoof, J. C. & Mulder, A. H. Eur. J. Pharmac. 46, 177–180 (1977).
Starr, M. S. Eur. J. Pharmac. 48, 325–328 (1978).
Giorgueff, M. F., Kernel, M. L., Glowinski, J. & Besson, M. J. Brain Res. 139, 115–130 (1978).
Arbilla, S. & Langer, S. Z. Br. J. Pharmac. 63, 389P–390P (1978).
Levi, G. & Raiteri, M. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 75, 2981–2985 (1978).
Snodgrass, S. R. Nature 273, 392–394 (1978).
Davies, J. & Watkins, J. C. Brain Res. 70, 501–505 (1974).
Olsen, R. W., Greenlee, D., Van Ness, P. & Ticku, M. K. in Amino Acids as Chemical Transmitters (ed. Fonnum, F.) 467–486 (Plenum, New York, 1978).
Galli, A., Zilletti, L., Scotton, M., Adembri, G. & Giotti, A. J. Neurochem. 32, 1123–1125 (1979).
Waddington, J. L. & Cross, A. J. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archs Pharmak. 306, 275–280 (1979).
Potashner, S. J. J. Neurochem. 32, 103–109 (1979).
Nistri, A. Experientia 31, 1066–1068 (1975).
Olpe, H. R. et al. Eur. J. Pharmac. 52, 133–136 (1978).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bowery, N., Hill, D., Hudson, A. et al. (–)Baclofen decreases neurotransmitter release in the mammalian CNS by an action at a novel GABA receptor. Nature 283, 92–94 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1038/283092a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/283092a0