Abstract
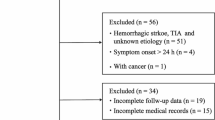
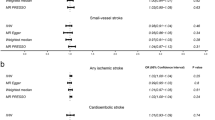
Serum VEGF level is regarded to be a biomarker for the diagnosis of stroke. Even though there have been published plethora of original articles describing higher blood VEGF concentrations since the 1970s, however, there is no any meta-analysis report for serum VEGF levels in the field of evidence-based medicine yet. A systematic review was performed by searching the online biomedical databases including retrieving 14 case–control studies including within-article subgroups after fulfilling the inclusion and exclusion criteria without the beginning date restriction, until 2020 for ischemic stroke patients. The Q quantity and I2% statistic index showed a high heterogeneity (84.895 and 84.687, respectively) and the random-effects model of meta-analysis was applied for further analyses. The meta-analysis on a total number of 769 stroke subjects and 621 controls found that the weighted pooled SMD for overall serum VEGF levels on different days of testing was 1.92 (95% CI, − 4.059–0.219, p value = 0.079) and the pooled SMD for overall serum VEGF levels on day 1 of testing was − 1.083 (95% CI, − 4.229–2.063, p value = 0.500). The meta-regression results demonstrated that different days of testing do not significantly affect serum VEGF concentrations in ischemic patients and actually their serum levels are time-independent. Based on the recently published studies, this meta-analysis showed that serum VEGF levels were not significantly associated with an ischemic stroke diagnosis. Thus, researchers may concern another ideal serum or cerebrospinal fluid-derived biomarker for stroke diagnosis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
González RG, Hirsch JA, Koroshetz W, Lev MH, Schaefer PW (2011) Acute ischemic stroke. Springer
Mendelow A D, Lo E H, Sacco R L, Faan MMF, Wong LK (2015) Stroke: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management, Elsevier Inc
Kini S, Memon F, Asgaonkar D (2019) Outcome in survivors of middle cerebral artery territory ischemic stroke: can it be predicted? J Assoc Phys India 6746
Hadi A, Bendriss L, Khatouri A (2018) The contribution of systematic implementation of cardiovascular explorations for the detection of cardiac sources of embolism in patients with stroke: about 230 patients. Ann Cardiol Angeiol 67(4):256–259
Farooqui AA (2013) Beneficial effects of propolis on neurological disorders. Springer, pp. 301-322
Aho K, Harmsen P, Hatano S, Marquardsen J, Smirnov VE, Strasser T (1980) Cerebrovascular disease in the community: results of a WHO collaborative study. Bull World Health Organ 58(1):113
Torres-Aleman I (2000) Serum growth factors and neuroprotective surveillance: focus on IGF-1. Mol Neurobiol 21(3):153–160
Jin KL, Mao XO, Greenberg DA (2000) Vascular endothelial growth factor: direct neuroprotective effect in in vitro ischemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci 97(18):10242–10247
Greenberg DA, Jin K (2013) Vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGFs) and stroke. Cell Mol Life Sci 70(10):1753–1761
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, The P G (2009) Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 6(7):e1000097
Higgins JPT, Thompson SG (2002) Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med 21(11):1539–1558
Faraone SV (2008) Interpreting estimates of treatment effects: implications for managed care. P T 33(12):700–711
Matsuo R, Ago T, Kamouchi M, Kuroda J, Kuwashiro T, Hata J, Sugimori H, Fukuda K, Gotoh S, Makihara N (2013) Clinical significance of plasma VEGF value in ischemic stroke-research for biomarkers in ischemic stroke (REBIOS) study. BMC Neurol 13(1):32
Giordano M, Ciarambino T, D’Amico M, Trotta MC, Sette D, Marinella A, Marfella R, Malatino L, Paolisso G, Adinolfi LE (2019) Circulating MiRNA-195-5p and-451a in transient and acute ischemic stroke patients in an emergency department. J Clin Med 8(2):130
Setyopranoto I, Sadewa AH, Wibowo S, Widyadharma IPE (2019) Comparison of mean VEGF-A expression between acute ischemic stroke patients and non-ischemic stroke subjects. Open Access Maced J Med Sci 7(5):747
Xue L, Chen H, Zhang T, Chen J, Geng Z, Zhao Y (2017) Changes in serum vascular endothelial growth factor and endostatin concentrations associated with circulating endothelial progenitor cells after acute ischemic stroke. Metab Brain Dis 32(2):641–648
Slevin M, Krupinski J, Slowik A, Kumar P, Szczudlik A, Gaffney J (2000) Serial measurement of vascular endothelial growth factor and transforming growth factor-β1 in serum of patients with acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 31(8):1863–1870
Mykhalojko O, Mykhalojko I (2017) Some biochemical changes in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Ukr Biochem J 89(3):31–35
Gavaghan DJ, Moore RA, McQuay HJ (2000) An evaluation of homogeneity tests in meta-analyses in pain using simulations of individual patient data. Pain 85(3):415–424
Higgins JPT, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327(7414):557
Geiseler SJ, Morland C (2018) The janus face of VEGF in stroke. Int J Mol Sci 19(5):1362
Kaya D, Gürsoy-Özdemir Y, Yemisci M, Tuncer N, Aktan S, Dalkara T (2005) VEGF protects brain against focal ischemia without increasing blood–brain permeability when administered intracerebroventricularly. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25(9):1111–1118
Acknowledgments
We appreciate Ilam University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The present study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Ilam University of Medical Sciences (IR.MEDILAM.REC.1398.187).
Additional information
Article highlights
• The association between serum VEGF concentrations and ischemic stroke detection was investigated using meta-analysis.
• The included studies (systematic review) were heterogeneous and the random-effects model was applied.
• The pooled SMD for overall serum VEGF levels on different days of testing was 1.92 (95% CI, − 4.059–0.219, p value = 0.079).
• The pooled SMD for overall serum VEGF levels on day 1 of testing was − 1.083 (95% CI, − 4.229–2.063, p value = 0.500).
• Based on the included studies, serum VEGF levels were not significantly associated with an ischemic stroke diagnosis.
• Researchers may concern another ideal serum or cerebrospinal fluid-derived biomarker for the near future.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seidkhani-Nahal, A., Khosravi, A., Mirzaei, A. et al. Serum vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) levels in ischemic stroke patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of case–control studies. Neurol Sci 42, 1811–1820 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-020-04698-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-020-04698-7